- Anti Ageing At A Glance
- Biophysical Skin Changes - In-Depth Analysis
- Epidermis - The First Skin Layer
- Dermis - The Second Skin Layer
- Hypodermis- The Deepest Skin Layer
- Visible Skin Signs Of Ageing
- What Causes Skin Ageing? A Summary
- CRES Principles - A Summary
- The "C" Of CRES Principles: Cleanse
- The "R" Of CRES Principles: Revitalise
- The "E" Of CRES Principles: Exfoliate
- The "S" Of CRES Principles: Stimulate
-
Injectables
-
Botox -
Dermal
fillers -
Lip Fillers -
Non Surgical
Nose Job -
Chin Filler -
Under Eye Circles
(Tear Trough) -
Non Surgical
Face Lift -
Masseter Botox -
Jawline Filler -
Cheek Fillers - Calf Reduction
- Nefertiti Lift (Platysma) & Turkey Neck Bands
- Bunny Lines (Nose Wrinkles)
- Lip Flip
- Trigger Point Release
- T-Zone Oily Skin
- Dimpled Chin
- Nasal Flaring
- Gummy Smile
- Bruxism / TMJ
- Migraines / headaches
- Neck lines
- Forehead Indentations
- Profhilo
- PDO threads
- Hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating)
- Fat Dissolving
-
-
Skin & Body
-
 V i s i t
V i s i t
- Chemical Peel
- Peel To Reveal Popular
- PRP (Vampire Facial)
- Prescription Grade Skin Care Popular
- Charity A Peel
- Hydrafacial
- Micro Needling (electronic) Popular
- Acne Treatments
- Facial Thread Veins
- Leg Veins (Spider/Thread Vein)
- Skin Tag Removal
- Ageing Skin Concerns
- Hyperpigmentation
- Facial Volume Loss
- Lines & Wrinkles
- Sun Damage
- Stubborn Fat Deposits
- Black Heads & White Spots
- Jawline, Jowls & Double Chin
- Cellulite
- Tired Eyes
- Neck - Lines, Wrinkles & Cords
-
- Glow & Go TM Skin Shop
- Book an Appointment Book
- CosmeShop
- Cosmetic Surgery
- CosmeTalk
-
COSMESURG| Surgical
-
| Professional EducationHARLEY STREET
INSTITUTE -
| Skin CareHARLEY STREET
FORMULATIONS -
GLOW & GO| Skin Bar Clinic
-
COSMETALK| Public Education
-
INJECTABLES
Injectables
-
SKIN & BODY
Skin & Body
-
COSMESHOP
-
COSMETALK
View All Posts
Dermal Fillers Before And After – Get The Better Version Of Yourself Today
It is true! Beauty industry has been revolutionized, aesthetic treatments have been personalized and new beauty… - ABOUT US& Treatment Criteria
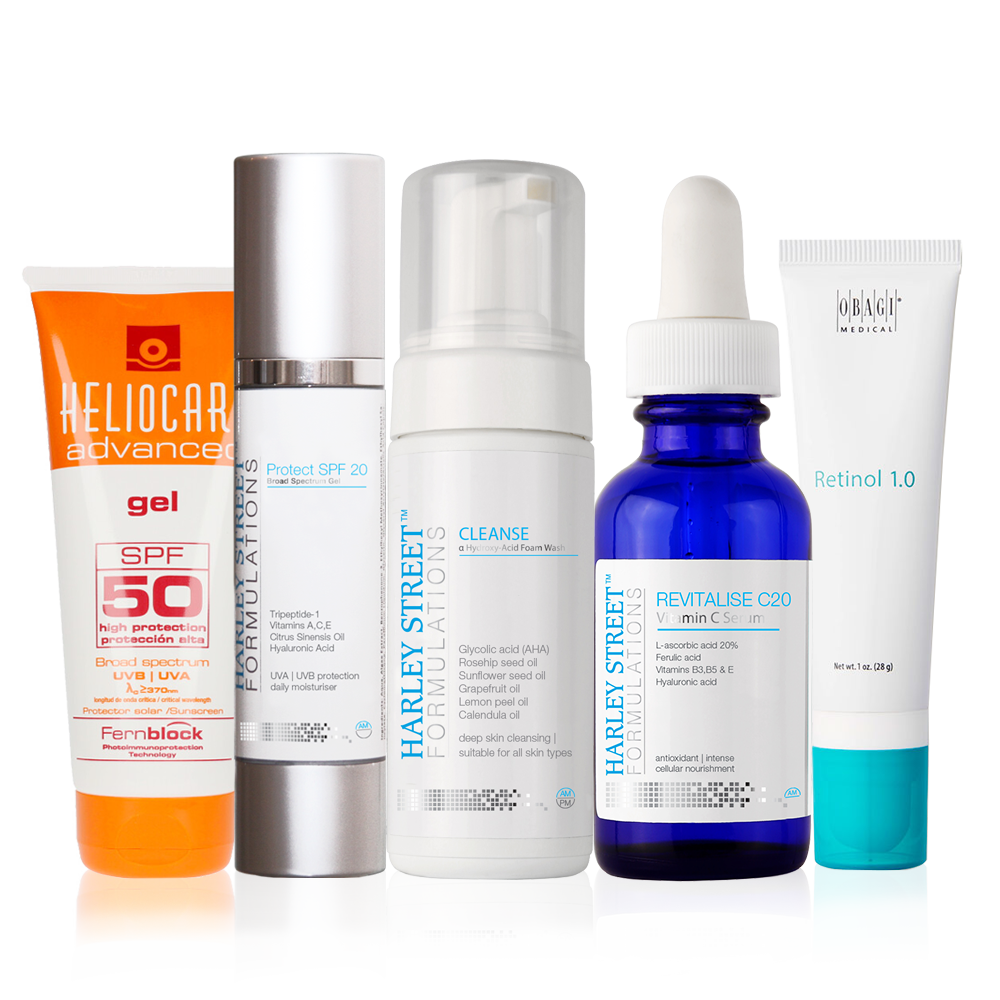
The “R” Of CRES Principles: Revitalise
Skin is a very delicate organ that is constantly exposed to visible and invisible harmful factors. They can affect it in so many bad ways, leading to premature ageing and skin diseases. While some of such harmful agents can be seen and hence can be avoided, other cannot be. Never forget that your eyes may remain unaware of some silent damage going on every minute.
As mentioned in the Cleanse portion, dust, debris, and dead skin cells can be removed and tackled by adopting a proper cleansing routine using right kind of ingredients. But is that enough? Not at all! This is the visible part of harmful agents that you are preventing. Invisible harmful agents are still there, doing their job silently that becomes apparent with the time.
What Are The Factors That Lead To Silent Damage?
So what are the most common invisible agents that cause harm to your skin? They can be both external and internal. All these factors basically produce some free radicals that further damage your skin cells. While talking about external factors, invisible spectrum of sunlight is the biggest culprit. Ultraviolet (UV) rays fall under this category.
Internal factors are different reactions which produce free radicals in your body.
What Are Ultraviolet (UV) Rays?
Ultraviolet (UV) rays are present on one extreme of sun spectrum and they cannot be seen with human eye. There are different types of these rays. The ones you are concerned with include UVA and UVB rays. Out of these both, UVA are specifically involved in making your skin age.
And guess what the scary thing about these rays is? They are present even on a cloudy day! So if you are happy that weather is nice and cloudy and you can set out today without any precautions, you are wrong. They can even penetrate your glass windows so you are not safe even indoors.
How Internal Environment Of Your Body Damages Your Skin Cells?
There are millions of small reactions going on in your body each and every moment. Your body is like a factory where different useful products are formed along with some wastes. Such wastes are byproducts of reactions occurring in your body. The most important byproducts that can be damaging for your skin are free radicals that can cause damage.
How Does The Damage Actually Occur?
The answer is, FREE RADICALS! They are the root cause. Free radicals are highly reactive species that have an unpaired electron and they are constantly looking for some other molecule to react with. When such reactive free radicals are formed in your skin, the handiest molecules to react with are the components of your skin cells.
Your skin cells are composed of various parts. From cell membrane to the nucleus, there are many different molecules that make a cell up. Lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins are the basic structural components of every cell in your body, including skin cells. So when such reactive free radicals are formed, they end up reacting with your cellular components, leading to a damaged and useless cell.
When a cell is damaged, a whole new cascade begins. They damage cell no longer performs its basic function so it is of no use. Your skin has mechanism where it controls and regulates such cells. At this stage where a cell stops functioning, a cell has to die. It also happens by the process of apoptosis where the cell itself commits suicide.
So a damaged cell finally dies. When a cell dies, there is a need to replace it with a new cell. Your skin turnover decreases with age and it may not produce as much new cells as free radicals kill. This leads to skin ageing.
Free radicals also lead to dyschromia and pigmentation by stimulating melanocytes present in your skin due to inflammation.
What Are The Visible Signs Of Free Radical Damage?
Free radical damage goes on with time. It might not be visible in start but as time passes, the signs of free radical damage start appearing. It is because the damage goes on with time and then a stage comes when damage become big enough to not to be masked. There are various visible signs of free radical damage that come under category of ageing. Following are a few most commonly experienced signs of them.
- Pigmentation of skin leading to melasma and uneven complexion
- Fine lines, specially around eyes and lips
- Saggy and wrinkled skin due to degradation of elastin and collagen fibres
- Loss of colour and fullness of your lips
- Age spots
- Appearance of thin veins on face and neck, known as spider veins
- Free radicals also cause inflammation, leading to post-inflammatory pigmentation (PIH)
All these changes collectively make your skin look aged, even if you are into your 20s. Read more about free radical damage here.
Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH)
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) causes darkened spots or large patches on the skin. This is due to excessive production of melanin by the cells in that area. This happens due to an inflammatory response in the skin due to an injury like burns, scratches, cuts, or bruises. In the event where the hyperproduction of melanin is in the upper layer of skin (epidermis), the pigmentation color is a darker brown and when it’s in the lower layer, blue or grey discoloration gets obvious.
To understand the underlying mechanism, let’s take the main culprit into consideration. When there is inflammation in the skin after an injury,oxygen is reduced into Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) which is hyper stimulated free radicals such as superoxide; hydrogen peroxide; hydroxyl radical; hydroxyl ion; and nitric oxide. These ROS have a role in cell signaling which then leads to apoptosis, gene expression, and the activation of cell signaling cascades as well as both intra- and intercellular messengers.
When these ROS are formed by various reasons, not only they stimulate the melanocytes to produces large amount of melanin but other pathways like melanogenesis due to NO induced tyrosine activity are also stimulated. In both ways, melanin concentration of that particular area is increased leading to PIH. The basis of immediate treatment is simple. It involves using antioxidants which suppress the formation of ROS and using tyrosine inhibitors which in turn suppress melanogenesis and cellular damage.
So Why Is It Necessary To Revitalise Your Skin?
The above discussion gives the answer! You skin is constantly undergoing invisible damage that becomes visible once it is big enough and beyond control. At that point, only cosmetic procedures help you the most. So prevention is better than cure.
While many of your skin cells are damaged every day, it is wise to repair them or prevent the damage right at the spot so that you don’t have to experience the cumulative effect.
What Revitalising Actually Is
Revitalising is the process of repairing free radical damage. It involves using specific products that have the ability to prevent and reverse free radical damage. You need to use such products constantly to make sure that your skin is being repaired every day.
What Products Revitalise Your Skin?
ANTI OXIDANTS! They have the ability to revitalise your skin. As it has been described earlier, free radicals are the main cause of all the skin damage leading to ageing. So prevention of ageing requires prevention of free radical formation.
Anti-oxidants can prevent free radical damage by fighting them. They prevent oxidative stress that leads to formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and other free radicals. So adding anti-oxidants to your skincare regime is a must.
What Are Different Kind Of Anti-Oxidants?
There is a variety of anti-oxidants that fall under two major categories. These categories are following.
- Direct anti-oxidants
- Indirect anti-oxidants
Let’s see the details.
Direct Anti-Oxidants
This type binds to free radicals directly therefore reducing the number of freely circulation radicals. This property makes their effectiveness and lifespan short-lived. Examples of these include:
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin D
- Minerals such as copper, zinc and manganese.
Indirect Anti-Oxidants
Unlike the direct anti-oxidants, this type supports the body to produce its own anti-oxidants. The benefits continue long after consuming such anti-oxidants. Indirect anti-oxidants are better at preventing premature ageing and related signs and symptoms. Indirect anti-oxidants also play a role in recycling bound direct anti-oxidants so that they can once more become effective in fighting circulating free radicals. For example, glutathione helps to recycle Vitamin E. Examples of indirect anti-oxidants include:
- Cruciferous vegetables such as cabbages and broccoli. The active antioxidants here are called sulforaphanes. Broccoli sprouts contain more antioxidant effects than mature broccoli.
- Berries and seeds with adequate fibre. They contain the antioxidant ellagic
- Glutathione
- Curcumin
- Resveratrol
- Green tea. The active indirect antioxidant here is epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG)
- Herbs such as ashwaganda, Licorice and the milk thistle
Anti-Oxidants With Mix Qualities
Some antioxidants exhibit both direct and indirect properties. Vitamin C is a classic example here. It is useful in not only directly binding to free radicals but it can also influence the recycling of Vitamin E.
While there are two major types, for optimal management of free radicals both direct and indirect anti-oxidants must work together. This happens in complicated biological processes occurring in human body.
Do All Kind Of Anti-Oxidants Have Same Potential To Prevent Damage?
The skin is prone to oxidative stress due to the continued exposure to the elements and particularly, the UV light. The endogenous anti-oxidants try to keep the skin free of these free radicals but with time they are depleted and signs of skin ageing set in. Topical application of anti-oxidants can help to support the body to keep the skin healthy. However, the question that raises here is “do all kind of anti-oxidants have same potential to prevent free radical damage?”.
The answer is NO! When you choose to topically apply an anti-oxidant, the factor that matters the most is molecular size. It should be small enough to allow penetration through skin because skin doesn’t allow transport of bigger molecules.
Which Are The Anti-Oxidants With Small Molecular Size?
Here is a list of such anti-oxidant agents that you should look for in your topical preparation to ensure positive results.
- Vitamin B3
- Vitamin E
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin A (retinol)
- Lycopene
- Resveratrol
- Hyaluronic acid
- Ferulic acid
- Glutathione
Let’s discuss a few important of them in detail.
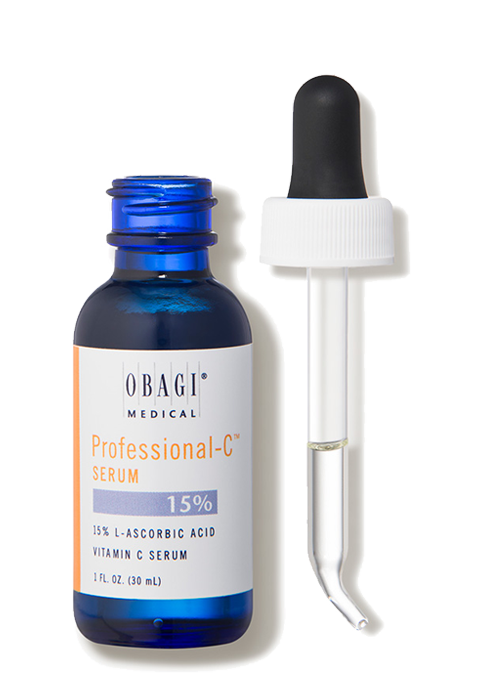
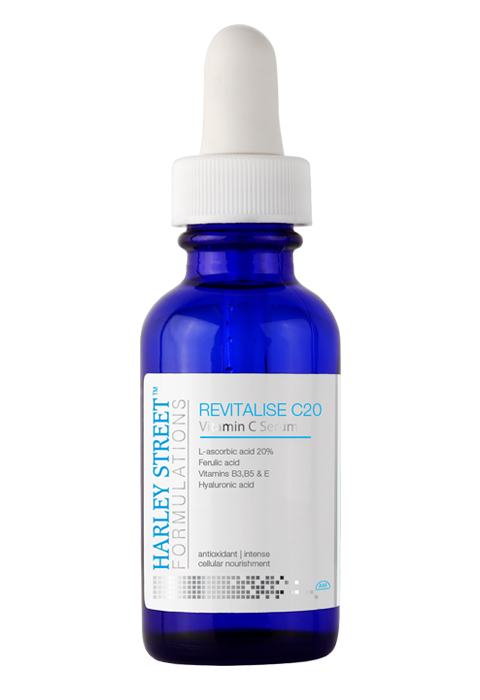
Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid)
You must have heard a lot about benefits of vitamin C for your skin and general health. Well, what you heard is not wrong. Vitamin C actually is a very effective and efficient agent as an anti-oxidant. It is not synthesized in the human body so taking it from external sources is also necessary. Deficiency of vitamin C can lead to various diseases like scurvy. And the plus point is that it doesn’t only prevents skin ageing but is also good for your general health as it helps preventing various cancers, cardiovascular diseases, and cataracts.
Now let’s look into its benefits when applied topically.
- The most important benefit of vitamin C is that it prevents free radical damage. Vitamin C donates free electron to the ROS, therefore neutralizing the free radicals and reducing the processes that eventually lead to collagen breakdown. Oxidised forms of Vitamin C can be converted back to Vitamin C by an enzyme.This is a special property of Vitamin C as an antioxidant because it can continue offering free radical scavenging effects for long.
- It prevents sun damage and improves sun protection when combined with sunscreen. It is equally effective against UVA (230mm-400mm) and UVB (290mm 320mm).
- Addition of ferulic acid increases the efficacy of Vitamin C by up to eight times. The commonly used formula is 15% Vitamin C, 1% Vitamin E, and 0.5% Ferulic.
- It stimulates collagen synthesis in many ways. It serves as a cofactor for the enzymes which are responsible for cross-linking and stabilising collagen molecules. It stimulates collagen gene expression via a cascade reaction. It directly activates transcription of collagen synthesis and stabilises pro-collagen mRNA. Therefore, it significantly improves wrinkles and skin hydration.
- Vitamin C also brightens your skin. It reduces tyrosinase kinase activity and decreases peri-follicular pigmentation. It is a non-toxic interrupter of melanogenesis.
- It also works as an anti-inflammatory agent by inhibiting various different factors. It helps to prevent post-inflammatory hyper pigmentation (PIH) skin disorder due to high amounts of oxidative stress produced in response to injury.
The side effects of using vitamin C topically are not very strong or bothering. Stinging, dryness, and redness are a few side effects. They can be easily managed by stopping use and applying moisturiser. Toxic effects only show when hundred times higher dose than recommended dose is taken so basically they are rare.
Glutathione (GSH)- The MOAX (Mother Of All Anti-Oxidants)
The name says it all! Glutathione is the most potent and the most abundant naturally found anti-oxidant. It shares many of its functions with vitamin C. Functions are following.
- Glutathione reduces oxidative stress and hence prevents free radical damage.
- It is proposed to bind to tyrosinase in its reduced form which inhibits the enzymatic pathways for production of melanin so it brightens the complexion. It is better than hydroquinone due to its multiple mechanism of actions like by preventing free radical-induced melanogenesis, increasing pheomelanin: eumelanin ratio (by facilitating the mechanism for switching between the two types of melanin),and by downregulating the pro inflammatory potential of leukotrienes.
- It also stimulates collagen production. It protects the keratinocytes from apoptosis under hyperglycaemic conditions. Visible effect on wrinkle reduction is shown in studies though the exact mechanism is unclear.
- Glutathione reduces pro-inflammatory factors and hence prevents inflammation.
Vitamin E
Vitamin E is a potent anti-oxidant agent and it has eight types. In human beings, alpha-tocopherol is the one that has been identified as important in meeting biological needs. Functions are following.
- It prevents oxidative stress and free radical damage.
- It regulates the immune system and makes it stronger.
- Vitamin C is hydrophilic and Vitamin E is lipophilic. Synergistically, they protect the respective cellular compartments by reducing premature cell apoptosis and thymine dimer formation (DNA Damage). There is notable protection against UVB rays effects when the two vitamins are used in combination.
Ferulic Acid
Ferulic acid is found naturally in many plants. It is generally accepted that it is one of the strongest antioxidant known. In cosmetics, it is used in some skin products in conjunction with other antioxidant ingredients such as vitamin C and E. Functions are following.
- It prevents free radical damage.
- It stabilizes vitamin C. Although vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant, it is unstable on exposure to UV light.
- Ferulic acid improves the efficacy of Vitamin C and E in skin products. When ferulic acid is added to the two vitamins, the synergistic effects is up to eight times that of vitamin C alone and twice that of the two vitamins together.
Vitamin B3
Vitamin B3, also called niacinamide is known for a wide range of health benefits. These include cardiac, respiratory, nervous, and joints health support among many other benefits. Even when taken orally it helps in the maintenance of a healthy skin. Following are its benefits for your skin health.
- It works as an anti-oxidant and prevents free radical damage.
- It helps in the maintenance of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide enzymes. These are needed for the production of energy at the cellular level and lipid synthesis. These two mechanisms are important for cell growth.
- Specific skin disorders that improve with vitamin B3 use include hyperpigmentation and other skin colour problems.
Vitamin A
Vitamin A is a fat soluble vitamin which is good for ophthalmic health, neurological functions support, healthy skin, healthy bones, and immune support.The main sources of vitamin A are through diet in foods such as milk, brightly coloured and dark leafy vegetables, animal organs such as the liver and eggs. Nutritional supplements containing the vitamin are also available. Many cosmetic products have vitamin A as an ingredient. Skin symptoms of vitamin A deficiency include dryness, scaly and thickened skin. Benefits are following.
- It is a good anti-oxidant that prevents skin damage.
- Isotretinoin, a synthetic form of vitamin A, is one of the best choices for stubborn acne.
- Vitamin A works by acting on the retinoic acid receptors. These stimulate the skin to produce more collagen, hasten desquamation, reduce inflammation and support the immune system. All these result in a newer and youthful looking skin.
- Vitamin A improves skin permeability. This is important for both cosmetic and dermatological issues.
What Role Does Nutrition Have In Your Skincare?
Well, it’s not only the topical treatment with anti-oxidants that matters for your skin health. Your diet too has an important role. Studies show that signs and symptoms observed on the skin can be delayed or in some cases, improved by using certain nutritional supplements. These are the supplements with anti-oxidant properties that help in reducing excess free-radicals in the body.Although these supplements are all free radicals scavengers, they do this in different ways and in different cell compartments. Some of the mechanisms antioxidant nutritional supplements use to manage free radicals include the following.
- Direct free radicals neutralization
- A reduction in reactive oxygen species (ROS) production through iron quenching
- Reduces peroxide and reverses damage already caused by the free radicals
- By the metabolism of lipids (short chain fatty acids and cholesterol esters) to neutralize ROS
Nutrition is the best source of anti-oxidants. It is the best source to derive vitamin C, E and carotenoids. Copper and selenium are two important trace elements that are also obtained from the diet. So taking a healthy and balanced diet is key to a healthy and youthful skin.
Some Agents Help With PIH AndMelasma As Well
PIH and melasma are important signs of skin ageing. Uneven skin tone bothers and causes cosmetic issues. There are various important agents available in the market within skin care products that can help fading away hyperpigmentation and even out your skin tone. Some important agents are:
- Kojic acid
- Mandelic acid
- Azelaic acid
Kojic Acid
The cosmetic preparation of Kojic acid usually used is of 1% concentration. It is a fungal metabolite that is commonly produced by A. acetobacter and Penicillium fungi.It suppresses tyrosinase activity by chelating copper. This can lead to brightening of the skin. Kojic acid is commonly combined with glycolic acid in formulations to make it more effective. It can be used twice daily for 1-2 months or until desired effects are achieved.
Side effects are allergy and dermatitis due to high concentrations.
Mandelic Acid
Mandelic acid is derived from almonds and diluted with hydrochloric acid and is an aromatic alpha hydroxyl acid. It is used as antibacterial, oral antibiotic and as a chemical peel. It is also used in the management of rosacea and telangiectasia. It is a mild exfoliating agent and promotes vascular turnover and regeneration. It has good results in fading away hyperpigmentation.
Azelaic Acid
Its clinical effectiveness is partly thought to be due to inhibitory action on neutrophil-generated reactive oxygen species (free radicals) which reduces both oxidative tissue injury at inflammatory sites and melanin production.It inhibits energy production and DNA synthesis of hyperactive melanocytes as well exhibiting anti-tyrosinase activity (competitive inhibitor of tyrosinase). This is why it is used as a first choice for treatment of PIH.
The next step of skin care according to CRES principles is Exfoliate. Click here to read.
Further Reading from Skin Ed
CosmeTalk Articles
Testimonials #Cosmestories
2
I had a botox treatment with cosmodocs. I found the price very reasonable. Even better the results were excellent. I will definitely use this service again.” – BH
3
I am a very satisfied customer of Cosmedocs – I’ve had three facial areas treated with Anti-Wrinkle Injection at CosmeDocs in recent years, and find the treatment swift, thorough and effective. Also, Dr Haq’s pleasant and friendly manner makes the treatment as painless as possible!” – CFSP
CosmeShop

-See more products