- Anti Ageing At A Glance
- Biophysical Skin Changes - In-Depth Analysis
- Epidermis - The First Skin Layer
- Dermis - The Second Skin Layer
- Hypodermis- The Deepest Skin Layer
- Visible Skin Signs Of Ageing
- What Causes Skin Ageing? A Summary
- CRES Principles - A Summary
- The "C" Of CRES Principles: Cleanse
- The "R" Of CRES Principles: Revitalise
- The "E" Of CRES Principles: Exfoliate
- The "S" Of CRES Principles: Stimulate
-
Injectables
-
Botox -
Dermal
fillers -
Lip Fillers -
Non Surgical
Nose Job -
Chin Filler -
Under Eye Circles
(Tear Trough) -
Non Surgical
Face Lift -
Masseter Botox -
Jawline Filler -
Cheek Fillers - Calf Reduction
- Nefertiti Lift (Platysma) & Turkey Neck Bands
- Bunny Lines (Nose Wrinkles)
- Lip Flip
- Trigger Point Release
- T-Zone Oily Skin
- Dimpled Chin
- Nasal Flaring
- Gummy Smile
- Bruxism / TMJ
- Migraines / headaches
- Neck lines
- Forehead Indentations
- Botox Forhead Lines
- Botox Crows Feet
- Botox Frown Lines
- Profhilo
- PDO threads
- Hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating)
- Fat Dissolving
-
-
Skin & Body
-
V i s i t
- Chemical Peel
- Peel To Reveal Popular
- PRP (Vampire Facial)
- Prescription Grade Skin Care Popular
- Charity A Peel
- Hydrafacial
- Micro Needling (electronic) Popular
- Acne Treatments
- Facial Thread Veins
- Leg Veins (Spider/Thread Vein)
- Skin Tag Removal
- Ageing Skin Concerns
- Hyperpigmentation
- Facial Volume Loss
- Lines & Wrinkles
- Sun Damage
- Stubborn Fat Deposits
- Black Heads & White Spots
- Jawline, Jowls & Double Chin
- Cellulite
- Tired Eyes
- Neck - Lines, Wrinkles & Cords
-
- Glow & Go TM Skin Shop
- Book an Appointment Book
- CosmeShop
- Cosmetic Surgery
- CosmeTalk
-
COSMESURG| Surgical
-
| Professional EducationHARLEY STREET
INSTITUTE -
| Skin CareHARLEY STREET
FORMULATIONS -
GLOW & GO| Skin Bar Clinic
-
COSMETALK| Public Education
-
INJECTABLES
Injectables
-
SKIN & BODY
Skin & Body
-
COSMESHOP
-
COSMETALK
View All Posts
Dermal Fillers Before And After – Get The Better Version Of Yourself Today
It is true! Beauty industry has been revolutionized, aesthetic treatments have been personalized and new beauty… - ABOUT US& Treatment Criteria
The “S” Of CRES Principles: Stimulate
Your skin is the largest organ of your body which is most exposed and hence most focused on. Whenever someone looks at you, it is your skin that sends out the first impression. A beautiful skin is considered as a standard of beauty. But can your skin always remain beautiful? Well, if you take proper care then obviously, it’s a yes!
What Does Happen To Your Skin Turnover Rate As You Age?
As you age, your skin ages too. Turnover rate falls many folds as compared with your youthful years. Your skin turnover time increases from 20 days to 30 or more days. This happens due to various reasons. First of all, your biological clocks slow down with ageing and slow down all the processes in your body including skin turnover. Another important point is hormonal changes. Estrogen is a hormone that makes your skin youthful and firm by increasing regeneration of fibres and turnover. As you age, the levels of many hormones including estrogen decrease that ultimately leads to decreased turnover. Other than that, your environment is full of harmful agents like pollution, UV rays that are there to damage your skin continuously. This is a steady turnover rate is necessary for healthy and pretty skin. However, this decrease in turnover rate due to ageing leads to dull and wrinkly appearance which is not very appealing and beautiful. To avoid this, a proper skincare regime is necessary. But can your skincare regime help with increasing skin turnover rate? Yes, it can!
How Can Skin Turnover Rate Be Increased In Your Older Years?
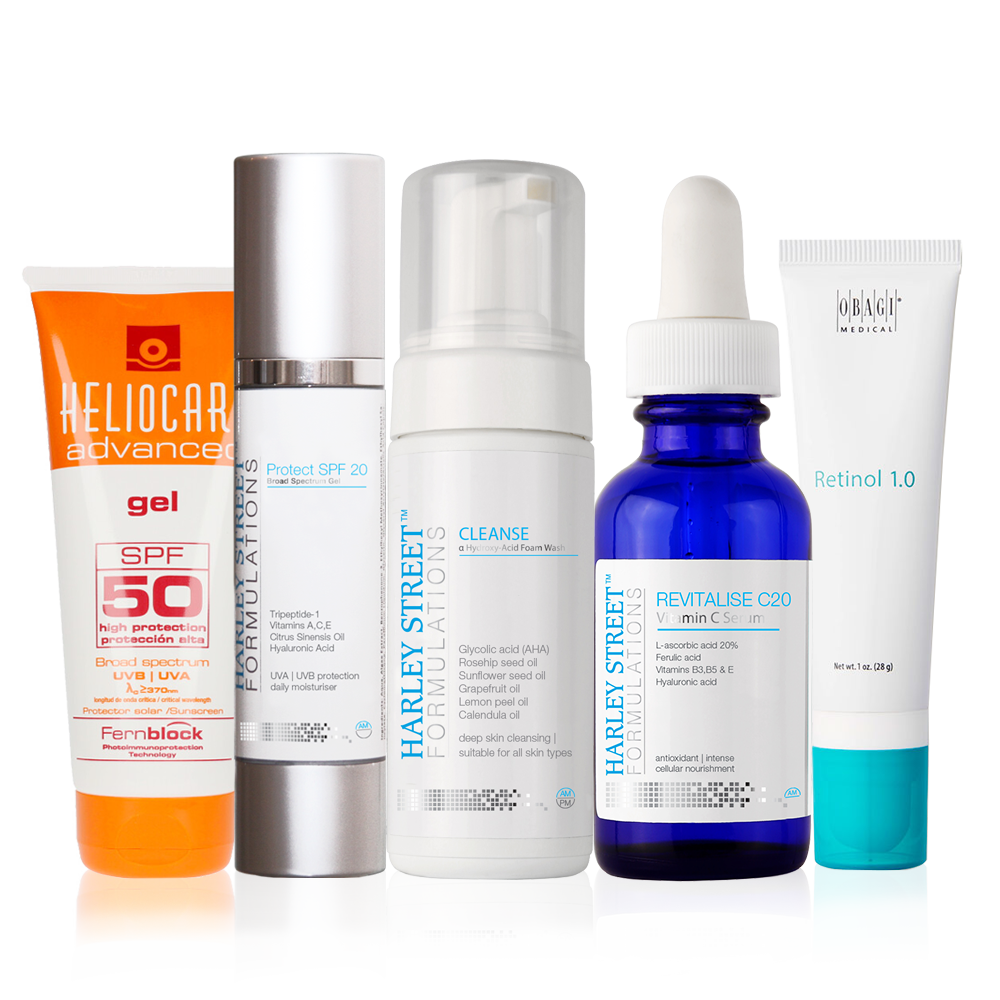
It asks for a proper skincare regime! CRES principles provide you with solution of your major skin problems and so they do regarding decreased skin turnover. Stimulate is the step of CRES principles that is the most important while dealing with decreased turnover.
How Can Skin Turnover Rate Be Increased In Your Older Years?
Stimulate is the process by which you get your skin working! There are various such chemicals and techniques that have the ability to activate your skin cells which in turn increases your skin turnover rate. When this turnover rate increases, your skin renews itself more frequently and it results in more even and youthful skin. It also makes sure that all essential skin elements like collagen and elastin fibres are also produced in good quantity to keep your skin firm and wrinkle free. Read more about skin structure here.
How Do Stimulating Procedures And Chemicals Work?
Long term management of skin ageing is dependent on the health and condition of the deeper layers of the skin where production of the cellular matrix takes place. The aim of cosmeceuticals and skin treatments such as chemical peels along with modalities that induce skin trauma is to activate mechanisms that are responsible for cellular signals within the cell nucleus. This is where regulation of collagen, elastin and other supporting structures’ production takes place. This can be triggered by either chemical stimulus or by the physical stimulus of the trauma of the treatment or both.
What Are Different Skin Stimulation Procedures And Chemicals?
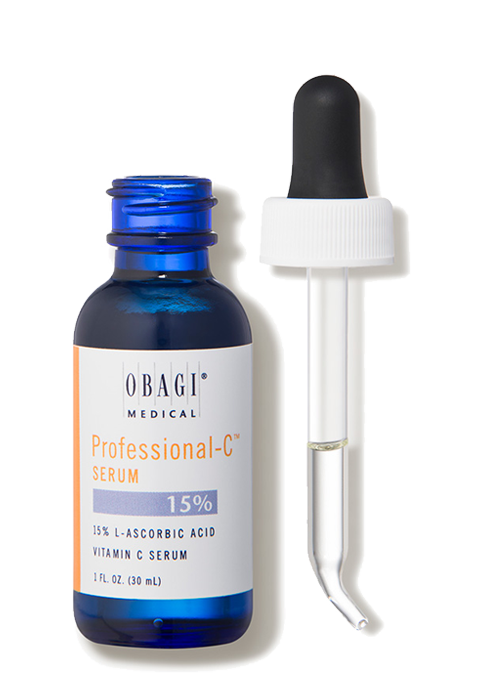
There are various difference techniques that can be employed when it is about stimulating your skin. However, not all of them are equally effective. Some work better than others. Also, a few are quite expensive than others. Common ingredients in skincare include high strength vitamins C and Retinoids. Peptides are newer ingredients that can also induce this mechanism.
Following is a list of a few commonly used methods for the purpose.
- L-Ascorbic Acid. See under Step 2: Revitalise. Many ingredients overlap in some benefits.
- Retinoids (Vitamin A & Derivatives)
- Peptides
- Medical needling
- Lasers/IPL
- Fractionated treatments
We will discuss chemical stimulating agents in more detail.
Retinoids:
Retinoids are very popular compounds in the world of dermatology for their wide spread implications and benefits. Let’s know more about them.
What are retinoids?
In cosmetic science, retinoids usually refer to lipid (fat) soluble topical application of a product that is derived from Vitamin A. Retinoid molecules can affect how cells multiply and behave. This affects cell stages such as differentiation, homeostasis, apoptosis and even the embryonic development.
Retinoids are useful in normalising hyper-keratinisation as well as shown strong anti-inflammatory and anti-pigmentary effects. They interfere with melanocyte transfer to keratinocytes, inhibit tyrosine kinase as well as increase pigment loss due to increase epidermal turnover. All this prevents various signs of ageing. They also are superior agents to treat acne which fails to respond to any other treatment.
What are different types of retinoids?
Beta-carotenes and other carotenoids compounds abundant in fruits and vegetables are some of the well-known. First generation retinoids in skincare include Tretinoin (retinoic acid), Retinol, and Retinal. In the second and third generation group are Etretinate, Tazarotene (Tazorac or Zorac) and Adapalene (Differin). Details of a few is given below for better understanding.
Retinal
Another name for retinal is retinaldehyde. It is sourced from animal proteins or from carotenoids (both alpha and betacarotenes). It performs closest to the prescription and is only retinoid acid with lesser skin irritation.
Retinol
This type of vitamin A is also referred to as Vitamin A1. It can be converted to retinal or retinoic acid. This way, it helps in promoting eye health (retinal) and the skin (retinol). Retinol is one of the most effective topical anti-ageing productsavailable in the cosmetic industry.
Retinoic acid
As mentioned above, retinoic acid is a derivative of retinol. This happens in two stages. The first step is a reversible reaction where retinol is converted to retinal. The second phase is an irreversible oxidation process where retinal is converted to retinoic acid. There are different types of biologically active retinoic acids. Each type act on specific retinoic acid receptors to trigger different cellular reactions.
Retinyl palmitate
This is a combination of a retinol ester and palmitic acid. It is a synthetic form of vitamin A. When used in topical skin products, it is absorbed and converted to retinol. It is finally converted to retinoic acid. This is the active form of vitamin A.
Retinyl acetate
This is a natural type of Vitamin A. It is also widely referred to as Vitamin A acetate and retinol acetate. When bound to retinoid receptors, it activates them. This initiates cell differentiation and at the same time decreases cellular proliferation. Studies have also shown that this form of vitamin can inhibit certain cell cancerous changes.
How do retnoids work?
Retinoids work by acting on the retinoic acid receptors (RAR). These are nuclear receptors that also behave as transcription factors. There are three main groups of RAR and they are:
1. Retinoic acid receptor alpha (RARa or RARa)
2. Retinoic acid receptor beta (RARb or RARb)
3. Retinoic acid receptor gamma (RARg or RARy)
Let’s look into different mechanisms which retnoids adopt to perform anti-ageing functions.
- The interaction between retinoids and specific RARs on the skin give rise to more collagen production. There is also an increased rate of desquamation which leads to the appearance of a newer and more youthful skin. For example, adapalene is a synthetic retinoid that is formulated to act on abnormal skin cells sloughing. In addition to this it also plays a role in cell differentiation and reduce harmful inflammation (Leyden 2001). Retinoids are also thought to have a direct effect on the skin’s immune response.
- According to Fisher and other research authors, tretinoin (a type of retinoid) effectively inhibits the effects of harmful matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). MMPs are known to induce severe collagen degradation. Such degradation makes the skin age faster. With this inhibition of the harmful properties of MMPs, retinoids promote the production of collagen. Retinoids specifically support the synthesis of type 1 collagen. This is the type needed in the skin in particular, very effective in people with photo-aged skin. In addition to this, it increases production and anchoring of fibrils. These are collagen type 4 cells that are also referred to as basement membrane collagen. These effects are easily seen with the use of tretinoin of 0.1% concentration.
- The effects of retinoids work right at the cellular level. This is where it abolishes cell abnormalities (atypia) as seen in psoriasis and improves the compacting of the stratum corneum. It also reduces melanin clumping in the basal cells and therefore induces a correction in the polarity of the keratinocytes.
What are the benefits of retinoids?
Retinoids are extensively used in skin care products and their benefits are well documented. These include:
- It is effective against skin conditions such as acne, psoriasis, ichthyosis, and keratoderma
- It is an effective preventive measure against photo-ageing
- It improves the texture of the skin and reduces wrinkles
- It improves the effects of sun-induced epidermal atrophy, dysplasia, keratosis and dyspigmentation
What are different side effects of retinoids?
As a lipid soluble derivative of vitamin A, the use of retinoids can lead to its accumulation in the body. This can lead to toxicity issues. Although this is unlikely to happen from topically applied products, other side effects have been observed on the skin. These include:
- Skin irritation, desquamation and erythema. These occur as a result of proliferation of keratinocytes and the severity is dose dependent. For example, tretinoin with a concentration of 0.1% exhibits three times more severe side effects than that of 0.025%.
- Dry skin due to an increase in trans-epidermal water loss (TEWL)
- Teratogenicity. It can cause embryonic disorders and so not recommended for use by pregnant or breastfeeding mothers. Also, doctors advice to not to plan a pregnancy for up to six months after retinoid use
- It causes an increase in photosensitivity due to stratum corneum thinning
To avoid these side effects, care should be taken while using retnoids and doctor’s instructions should be followed strictly. Using retnoids without proper guidance is not a good idea as they should be started in low dosage that can be increased later with time under supervision. Abrasive agents and procedures should not be used when using retinoids. Also, use of sunblock is advised to protect skin from sun damage as it becomes more prone to damage during such treatment. Read more about sunblocks here. Retnoids are also used in combination with hydroxyl acids because it reduces skin irritation.
Peptides And Matrikines
Peptides and matrikines are second most commonly used agents to stimulate skin for a better health. Let’s look into them as well.
What are peptides and matrikines?
Peptides are important components of the innate immune system. They exhibit a broad spectrum antimicrobial activity. There are two major groups of peptides called Defensives and Cathelicidins. The term “matrikines” was coined for designating peptides liberated by partial proteolysis of extracellular matrix macromolecules. Peptides may modulate proliferation, migration, protease production, or apoptosis. Matrikines may play a significant role in physiological or pathological processes such as wound healing or tumor invasion due to their nature of activity. The efficacy of peptides in cosmetic skin care is dependent like any other ingredient on their concentration. Due to their high costs of development,this concentration tends to be on the lower end in most cosmetic formulations.
What are the names of different peptides and matrikines?
There are various available peptides and matrikines that can help with anti-aging but usage is limited because of various reasons like cost etc. Following is a list of commonly used and effective agents in this group.
- Matrixyl synthe’6 (PalmitoylTripeptid-38)
- Matrixyl 3000
- Syn-coll
- Argireline
- Leuphasyl
- Melanostatine-5
- Aldenine
- Peptamide 6
How do peptides benefit your skin?
Following are some benefits we are concerned with.
- Peptides are fractions of proteins. There are various proteins found in skin. Collagen and elastin are the most important one as their deficiency leads to skin ageing. Peptides and matrikines make sure that your skin has ample amount of collagen. They encourage collagen production.
- Peptides and martikines remove wrinkles. They are a less expensive alternative to botox. They work by relaxing small facial muscles and hence minimise wrinkles
- They have a protective effect
- They have skin brightening properties
- Some of them are cellular detoxifier
- Peptide and matrikines decrease skin roughness and give your skin a smooth look
The best thing about peptides is that they are safe for your skin.
What Is CRES-(P)?
P notifies “Protect” here. This step is often added to CRES regime and indicates the importance of skin protection against harmful environmental factors. To know more about this step, read our section on sun protection and sunscreens of different kinds.
All the above discussion, from the very first step of CRES principles to the last one, proves that ageing can be prevent by taking preventive measures in form of a good skincare regime. So start taking care of your skin from today!
Further Reading from Skin Ed
CosmeTalk Articles
Testimonials #Cosmestories
2
I had a botox treatment with cosmodocs. I found the price very reasonable. Even better the results were excellent. I will definitely use this service again.” – BH
3
I am a very satisfied customer of Cosmedocs – I’ve had three facial areas treated with Anti-Wrinkle Injection at CosmeDocs in recent years, and find the treatment swift, thorough and effective. Also, Dr Haq’s pleasant and friendly manner makes the treatment as painless as possible!” – CFSP
CosmeShop

-See more products