Sunspots and wrinkles are probably not things you signed up for when you first came into existence. After all, we were born with great and smooth skin as babies.
To make matters even worse you may even feel that the people around you might not accept you with all these “apparent flaws” that have come with age. Knowing that those very same people may be feeling the exact same way you do, makes very little difference, you still want to look as good (young, healthy) as you possibly can.
Pigmentation Happens – But Treatable
Yes, we all have pigmentation to a certain degree after crossing 20 years of age. The question is how do we medically deal with it? We would love to hear from people what they have been using so far.
Skin pigmentation and medical treatments
Skin cells called melanocytes are responsible for the production of melanin, the substance which gives skin’s color. In some people, production of melanin is naturally higher therefore their skin is darker, while in others skin’s less pigmented and has a lighter tone due to a reduced production of this substance.
Although both these situations are normal, there are also people in which skin’s production of melanin is altered and pigmentation disorders appear. And we’re not talking about individuals whose skin is coloured differently due to race or geographical area, but by people in which hypo- or hyper-production of this substance is triggered by harmful environmental agents or by ailments.
Melanocytes are found in the top layers of the skin so it’s quite easy for these cells to get damaged and to start producing abnormal amounts of melanin.
Why do skin pigmentation disorders occur?
Generally speaking, pigmentation disorders can appear whenever the body produces too much or too little melanin, causes of this condition varying from autoimmune conditions to genetic inheritance and sun damage. In fact, excessive exposure to sunlight seems to be the leading cause of abnormal colouration of skin. But birth control pills and pregnancy can also cause pigmentation disorders and aging triggers such problems as well.
Listed below are the most common causes of pigmentation disorders:
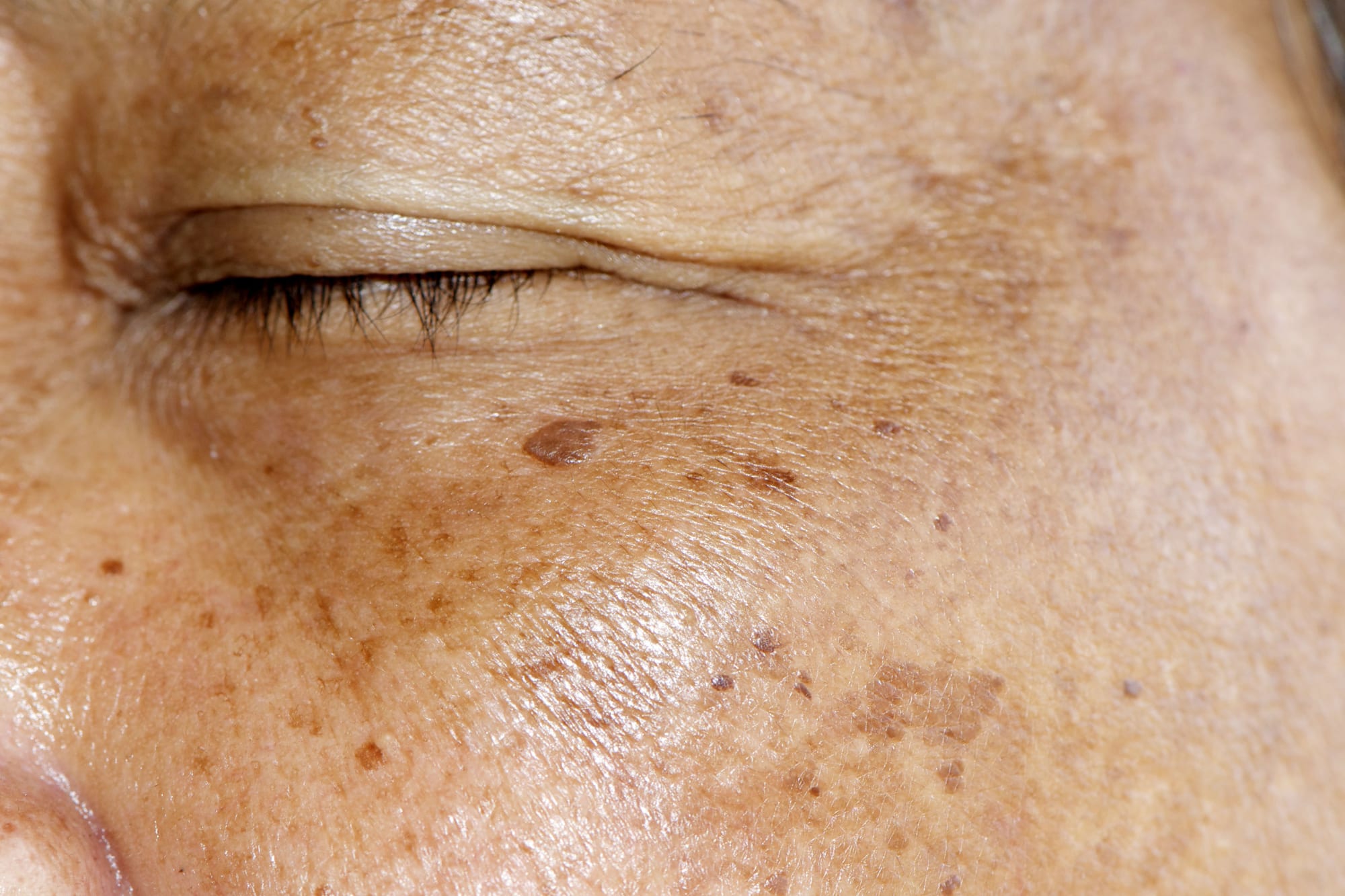
Sun damage – sun spots are probably the most common form of pigmentation disorder. They’re caused by excessive exposure to UV rays, which stimulate melanocytes to synthesize more melanin than usually.
Hyper-production of this pigment is needed for skin to absorb ultraviolet rays better and as long as it doesn’t exceed certain levels, this is a normal reaction. The increase in melanin levels causes the skin to darken or to tan, as we say. But when the amount of pigment is too high, freckles and so-called age spots form.
Pregnancy – hormonal changes taking place during pregnancy trigger the so-called melasma, condition manifesting through hyperpigmentation and referred to as “the mask of pregnancy”. This disorder leads to the occurrence of brownish or grayish patches on the forehead, cheeks and nose.
Oral contraceptive pills/hormone replacement therapy pills – just like pregnancy, these pills can trigger melasma, mainly due to their interaction with sun rays.
Inflammation – in some people hyperpigmentation is favored by the presence of an inflammatory process affecting the skin and triggered by burns, pimples, cuts or scrapes.
Medical conditions – in certain conditions, skin discolouration or hyperpigmentation can indicate an underlying ailment, such as endocrine disorders for example.
How pigmentation disorders manifest
Skin pigmentation disorders manifest mainly as:
- The already mentioned melasma, defined by irregular patches appearing on the face and affecting not only pregnant women but also men and non-pregnant females. It’s triggered by sun exposure, skin damage and acne lesions, as well as by pregnancy, as mentioned before.
- Albinism, or the absence of melanin, which is inherited and affects people of all ages and races. This condition is defined by the lack of coloured pigments in eyes, skin and hair.
- Vitiligo, defined by the development of white patches around the eyes and mouth as well as on the back of the hands. In rare cases discoloration affects knees, elbows, shins and the genital region also.
Can skin pigmentation be prevented?
Although not all the conditions associated with pigmentation disorders are threatening for one’s health, abnormal skin colouration affects one’s self-esteem and self-confidence levels for sure.
Fortunately, many cases of skin discolouration or hyperpigmentation can be prevented through simple measures, such as limiting the exposure to sunlight during critical hours, applying sunscreen and wearing scarves or hats for reducing the amount of radiation that can affect the skin.
Topical ointments and creams containing topical steroids, alpha hydroxyl acids, kojic or malic acids, vitamin C and E, tretinoin and hydroxyl quinine can also be used in preventing and reducing hyperpigmentation. However, if the condition is already present, one may require a more powerful treatment, such as the ones listed in the next section.
Medical treatments for skin pigmentation
As previously said, creams containing kojic acid, malic acid, vitamin C, retinol and the acid form tretinoin, as well as AHA (alpha-hydroxy acids) and PHA (polyhydroxy acids) can be successfully used as treatments for skin pigmentation disorders.
Skin lighteners containing hydroquinone 2-4% are also recommended to people with abnormal skin pigmentation. However, when creams don’t work and topical products aren’t powerful enough for restoring the skin’s balance and colouration, chemical peels, microdermabrasion and fractional laser treatments are further treatment options.
Melasma can be treated with home remedies such as over-the-counter skin-lightening creams or prescription creams containing higher doses of hydroquinone, retinoic acid and hydrocortisone. Also, prescription creams based on tretinoin, azelaic and kojic acid can be recommended. In case melasma already penetrated the skin, microdermabrasion, chemical peels and laser treatments will be recommended.
Microdermabrasion is a technique during which superficial layers of skin are exfoliated mechanically, surgeon using specific tools and materials, such as diamond flakes or crystals for removing dead and damaged cells, respectively a suction machine for lifting up skin after exfoliation. Procedure is simple and painless, time required for recovery being minimal.
Chemical peels act by removing dark cells in the superficial layers of the skin and stimulating the production of new cells. Depending on how strong the chemical peels are, separation of cells can go deeper into the skin.
Laser treatments such as the IPL (intense pulsed light) technique work by emitting light of a certain wavelength, which can break down pigments into smaller particles, eliminated by the organism on its own. Besides treating hyperpigmentation, laser treatments also improve skin’s texture, rejuvenate it and minimize pores and fine lines.
For vitiligo, non-prescription treatments include bronzers, makeup and skin stains, while medical treatments are:
- phototherapy, which stimulates melanin production
- excimer laser therapy, which delivers UVB light, increasing the production of skin-colouring pigment
- psoralens, drugs that increase skin’s sensitivity to light, helping it to get tanned.